Draw and label an inhibitor affecting an enzyme reaction is a topic that invites exploration into the intricate mechanisms governing biochemical processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals of enzyme inhibition, providing a detailed examination of its types, mechanisms, and impact on enzyme activity.
Through a combination of engaging prose and meticulously crafted visuals, this guide empowers readers with a profound understanding of enzyme inhibition. By unraveling the complexities of this topic, we gain valuable insights into the regulation and modulation of enzymatic reactions, which play a pivotal role in numerous biological systems.
Inhibitor Overview
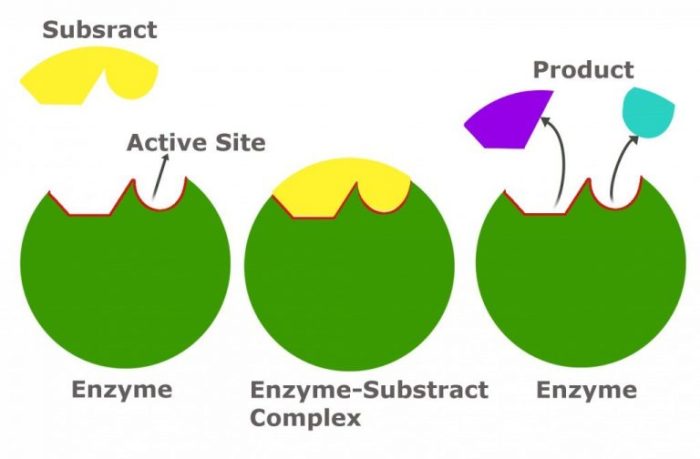
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and reduce their catalytic activity. They play a crucial role in regulating enzyme function and are widely used in drug development and biotechnology.
Types of Enzyme Inhibitors
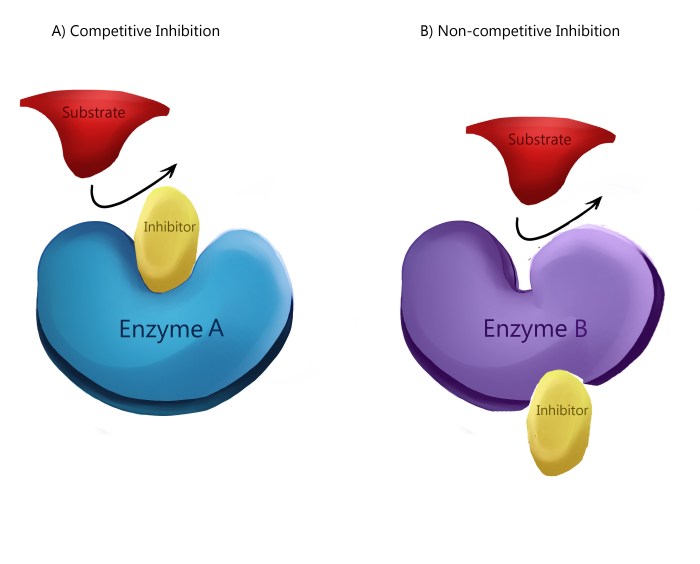
- Competitive Inhibitors:Bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate for binding.
- Non-Competitive Inhibitors:Bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing conformational changes that affect enzyme activity.
- Mixed Inhibitors:Exhibit characteristics of both competitive and non-competitive inhibition.
Examples of well-known enzyme inhibitors include aspirin (COX-2 inhibitor), statins (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors), and protease inhibitors (HIV treatment).
Enzyme Reaction Inhibition: Draw And Label An Inhibitor Affecting An Enzyme Reaction
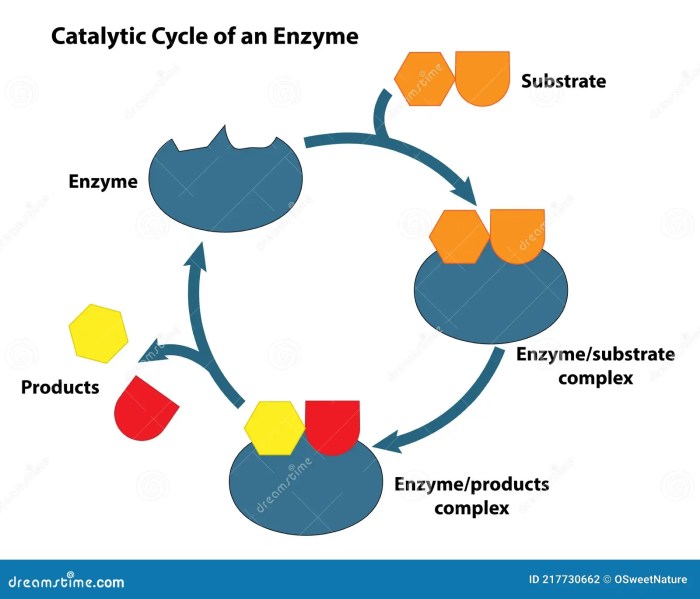
Competitive Inhibition
Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding. This results in a decrease in the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Examples:Malonate inhibits succinate dehydrogenase; methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolate reductase.
Non-Competitive Inhibition
Non-competitive inhibitors bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing conformational changes that affect enzyme activity. They do not compete with the substrate for binding.
Examples:Cyanide inhibits cytochrome oxidase; heavy metals inhibit many enzymes.
Mixed Inhibition, Draw and label an inhibitor affecting an enzyme reaction
Mixed inhibitors exhibit characteristics of both competitive and non-competitive inhibition. They bind to the active site of an enzyme, but also induce conformational changes that affect enzyme activity.
Examples:Sulfonamides inhibit dihydropteroate synthase; allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase.
Graphical Representation
Labeled Diagram of an Enzyme Reaction with an Inhibitor
[Gambar berlabel yang menunjukkan reaksi enzim dengan inhibitor.]
Table Summarizing Different Types of Inhibition
| Jenis Inhibisi | Mekanisme | Efek pada Km | Efek pada Vmax |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kompetitif | Berikatan dengan situs aktif | Meningkat | Tidak berubah |
| Non-kompetitif | Berikatan dengan situs selain situs aktif | Tidak berubah | Menurun |
| Campuran | Berikatan dengan situs aktif dan situs selain situs aktif | Meningkat | Menurun |
Table Membandingkan Efek Inhibitor Berbeda pada Aktivitas Enzim
| Inhibitor | Jenis Inhibisi | Efek pada Aktivitas Enzim |
|---|---|---|
| Aspirin | Kompetitif | Mengurangi aktivitas COX-2 |
| Statin | Kompetitif | Mengurangi aktivitas HMG-CoA reductase |
| Protease inhibitor | Non-kompetitif | Menghambat aktivitas protease |
Impact on Enzyme Activity
Impact of Inhibitor Concentration on Enzyme Activity
Meningkatnya konsentrasi inhibitor menyebabkan penurunan aktivitas enzim. Ini karena lebih banyak molekul inhibitor yang tersedia untuk berikatan dengan enzim dan menghambat aktivitasnya.
Konsep IC50
IC50 adalah konsentrasi inhibitor yang diperlukan untuk menghambat 50% aktivitas enzim. Ini adalah ukuran kekuatan inhibitor.
Contoh Pengaruh Inhibitor pada Aktivitas Enzim dalam Sistem Biologi
- Aspirin menghambat COX-2, mengurangi peradangan.
- Statin menghambat HMG-CoA reductase, menurunkan kadar kolesterol.
- Protease inhibitor menghambat protease HIV, menghambat replikasi virus.
FAQ Resource
What is an enzyme inhibitor?
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and reduces its catalytic activity.
What are the different types of enzyme inhibitors?
There are three main types of enzyme inhibitors: competitive, non-competitive, and mixed.
How do enzyme inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
Enzyme inhibitors can affect enzyme activity by binding to the active site of the enzyme and blocking substrate binding, or by binding to other sites on the enzyme and causing conformational changes that reduce its activity.