Make connections the plasma membrane and phospholipid structure – At the heart of every cell lies the plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer that orchestrates a symphony of life-sustaining processes. Delving into the intricate relationship between the plasma membrane and phospholipid structure, we embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of cellular communication, transport, and function.
Phospholipids, the building blocks of the membrane, possess a unique amphipathic nature, with hydrophilic heads drawn to water and hydrophobic tails repelled by it. This delicate balance gives rise to the lipid bilayer, a semipermeable barrier that both protects the cell and facilitates the exchange of essential molecules.
Plasma Membrane Composition and Structure: Make Connections The Plasma Membrane And Phospholipid Structure
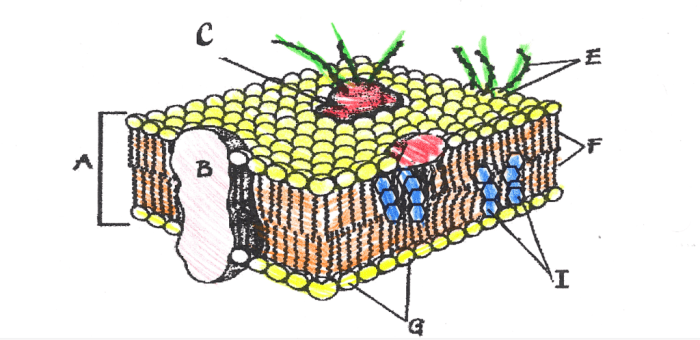
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds and protects the cell. It acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
The plasma membrane is composed primarily of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins.
Arrangement and Orientation of Phospholipids in the Plasma Membrane
Phospholipids are the major components of the plasma membrane. They are arranged in a bilayer, with their hydrophobic tails facing inward and their hydrophilic heads facing outward. This arrangement creates a selectively permeable barrier that allows certain substances to pass through the membrane while blocking others.
Detailed Illustration of the Plasma Membrane Structure

The plasma membrane is a dynamic structure that undergoes constant remodeling. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol molecules, and various proteins. The phospholipid bilayer is a semi-permeable barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings. Cholesterol molecules help to stabilize the bilayer and prevent it from becoming too rigid. Proteins are embedded in the bilayer and perform a variety of functions, such as transporting molecules across the membrane, signaling, and cell adhesion.
Phospholipid Structure and Properties
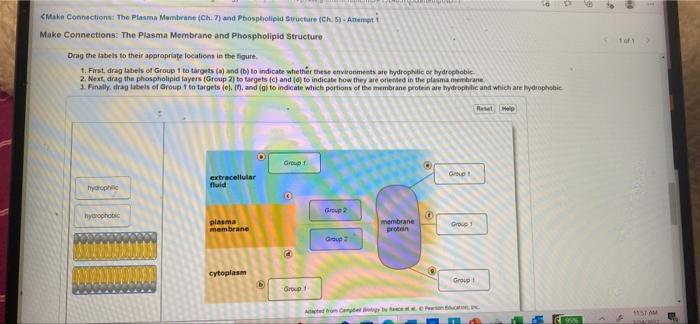
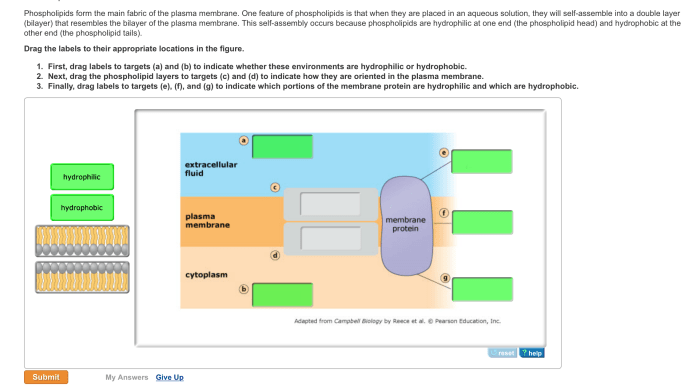
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, meaning they have both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-hating) regions. The hydrophilic head group is composed of a phosphate group and a glycerol molecule. The hydrophobic tail group is composed of two fatty acid chains.
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Properties of Phospholipids
The hydrophilic head group of phospholipids interacts with water molecules, while the hydrophobic tail group interacts with other hydrophobic molecules. This amphipathic nature of phospholipids allows them to form bilayers in aqueous environments.
Contribution of Phospholipid Structure to the Formation of the Lipid Bilayer
The bilayer structure of the plasma membrane is formed by the interaction of phospholipids with water molecules. The hydrophobic tail groups of phospholipids are sequestered away from water, while the hydrophilic head groups interact with water molecules. This arrangement creates a selectively permeable barrier that allows certain substances to pass through the membrane while blocking others.
Interactions between Phospholipids and Proteins
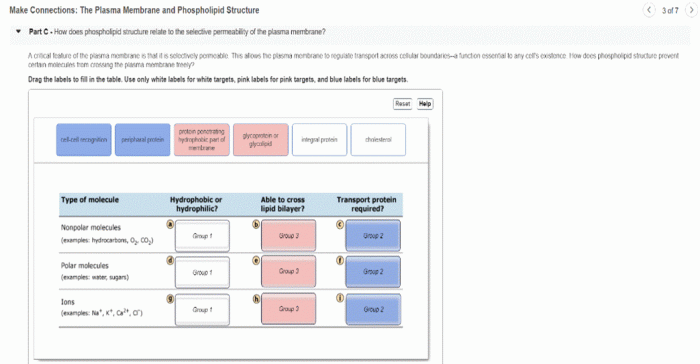
Proteins are embedded in the plasma membrane and play a variety of roles in cell function. They can be classified into two types: integral proteins and peripheral proteins.
Types of Proteins Associated with the Plasma Membrane
- Integral proteinsare embedded in the lipid bilayer and span the entire membrane. They are typically involved in transporting molecules across the membrane or signaling.
- Peripheral proteinsare attached to the surface of the lipid bilayer and do not span the entire membrane. They are typically involved in cell adhesion or signaling.
Protein-Lipid Interactions, Make connections the plasma membrane and phospholipid structure
Proteins interact with the lipid bilayer in a variety of ways. Some proteins are embedded in the bilayer, while others are attached to the surface of the bilayer. The interaction between proteins and lipids is important for maintaining the structure and function of the plasma membrane.
Effects of Protein-Lipid Interactions on Membrane Function
Protein-lipid interactions can affect the fluidity and permeability of the plasma membrane. Proteins can also interact with each other to form protein complexes that perform specific functions. These protein complexes can be involved in a variety of cellular processes, such as cell signaling, cell adhesion, and membrane transport.
Quick FAQs
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane serves as a protective barrier, regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the cell.
How do phospholipids contribute to membrane fluidity?
Phospholipids possess both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions, allowing them to form a flexible bilayer that can adapt to changes in temperature and pressure.
What role do proteins play in membrane function?
Proteins embedded in or associated with the membrane facilitate a wide range of cellular processes, including transport, signaling, and adhesion.