Describe what each letter stands for in the cvp graph. – In the realm of business analysis, the CVP graph emerges as a pivotal tool, offering insights into a company’s financial performance and decision-making. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this graph, deciphering the significance of each letter: Contribution Margin, Variable Costs, and Fixed Costs, to empower readers with a thorough understanding of its applications.
The CVP graph serves as a visual representation of a company’s cost and revenue structure, enabling businesses to analyze the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profitability. Understanding the components of this graph is crucial for effective planning and decision-making.
CVP Graph Introduction
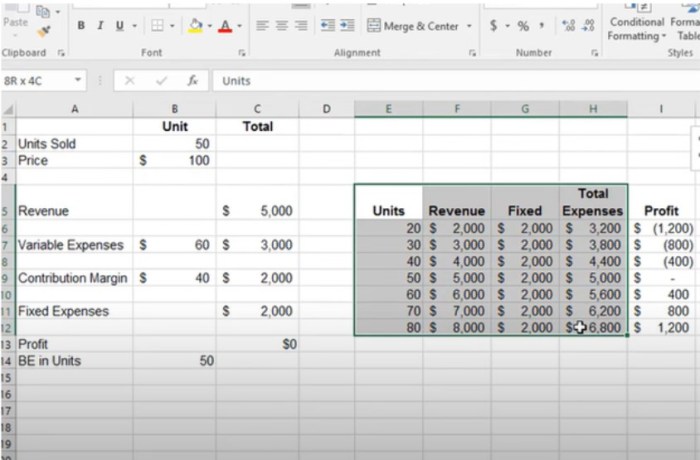
A cost-volume-profit (CVP) graph is a graphical representation of the relationship between costs, volume, and profit. It is a valuable tool for managers to understand how changes in activity levels affect profitability.
The CVP graph has three axes: sales revenue, costs, and profit. The sales revenue axis shows the total revenue generated by the company at different levels of activity. The costs axis shows the total costs incurred by the company at different levels of activity.
The profit axis shows the difference between sales revenue and costs at different levels of activity.
Letter C: Contribution Margin
Contribution margin is the difference between sales revenue and variable costs. It is an important measure of profitability because it shows how much of each sales dollar contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Contribution margin is calculated as follows:
Contribution Margin = Sales Revenue
Variable Costs
For example, if a company has sales revenue of $100,000 and variable costs of $60,000, its contribution margin would be $40,000.
Contribution margin can be used to make a variety of decisions, such as:
- Pricing decisions
- Product mix decisions
- Make-or-buy decisions
Letter V: Variable Costs
Variable costs are costs that change with the level of activity. Examples of variable costs include:
- Raw materials
- Direct labor
- Sales commissions
Variable costs are important because they affect the contribution margin and the profitability of the company.
The relationship between variable costs and contribution margin is as follows:
Contribution Margin = Sales Revenue
Variable Costs
As variable costs increase, the contribution margin decreases. This is because a larger portion of each sales dollar is used to cover variable costs, leaving less to cover fixed costs and generate profit.
Letter P: Fixed Costs, Describe what each letter stands for in the cvp graph.
Fixed costs are costs that do not change with the level of activity. Examples of fixed costs include:
- Rent
- Salaries
- Insurance
Fixed costs are important because they affect the break-even point and the profitability of the company.
The relationship between fixed costs and profitability is as follows:
Profit = Sales Revenue
- Variable Costs
- Fixed Costs
As fixed costs increase, the profit decreases. This is because a larger portion of each sales dollar is used to cover fixed costs, leaving less to generate profit.
Answers to Common Questions: Describe What Each Letter Stands For In The Cvp Graph.
What is the purpose of a CVP graph?
A CVP graph helps businesses visualize the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profitability, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and marketing.
How is Contribution Margin calculated?
Contribution Margin is calculated as the difference between sales revenue and variable costs.
What is the difference between variable and fixed costs?
Variable costs change with the level of activity, while fixed costs remain constant regardless of activity levels.