Comparing the articles of confederation and the constitution worksheet answers – Delving into the nuances of the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution, this exploration unveils the intricacies of these foundational documents that shaped the course of American history. Through a meticulous examination of their key differences, the evolution of the federal government, and the enduring impact on society, this guide illuminates the significance of these charters in shaping the American experience.
Comparing the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution: Historical Context: Comparing The Articles Of Confederation And The Constitution Worksheet Answers
The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, established a loose confederation of independent states with a weak central government. The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, including the lack of a strong executive, a national court system, and the inability to tax or regulate commerce, led to the need for a stronger central government.
The Constitutional Convention was held in Philadelphia in 1787 to revise the Articles of Confederation. The convention ultimately decided to scrap the Articles and draft a new constitution, which was ratified in 1788.
Timeline of Key Events, Comparing the articles of confederation and the constitution worksheet answers
- 1777: Articles of Confederation drafted
- 1781: Articles of Confederation ratified
- 1787: Constitutional Convention held
- 1788: Constitution ratified
Key Differences between the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution
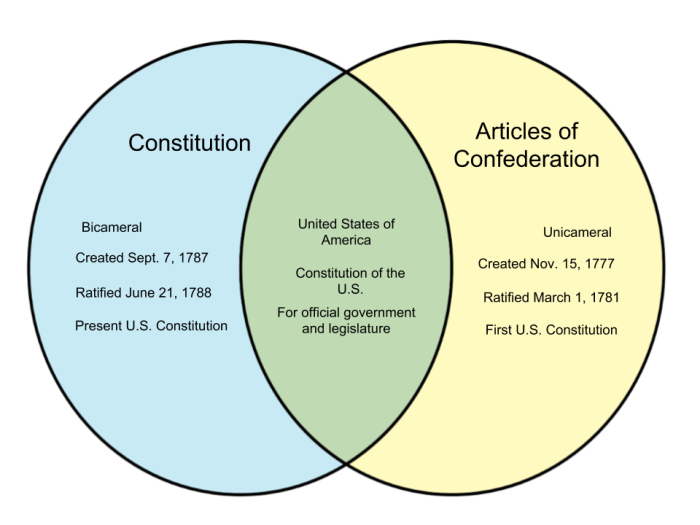
| Articles of Confederation | Constitution | |
|---|---|---|
| Central Government Powers | Weak, limited to foreign affairs, war, and postal service | Stronger, with powers including taxation, regulation of commerce, and maintenance of a military |
| State Powers | Considerable, including the power to tax, regulate commerce, and maintain a militia | More limited, with states retaining powers not delegated to the federal government |
| Taxation and Finance | No power to tax | Power to tax and borrow money |
| Commerce and Trade | No power to regulate commerce | Power to regulate commerce between states and with foreign nations |
| Foreign Policy | Limited to making treaties and declaring war | Expanded, with the president having the power to negotiate treaties and the Senate having the power to ratify them |
| Amendment Process | Required unanimous consent of all states | Requires ratification by three-fourths of the states |
The Structure and Powers of the Federal Government under the Constitution

The Constitution established a three-branch federal government:
- Legislative Branch:Congress, consisting of the Senate and House of Representatives, has the power to make laws.
- Executive Branch:The president, vice president, and cabinet departments are responsible for executing laws.
- Judicial Branch:The Supreme Court and lower federal courts interpret laws and resolve disputes.
The system of checks and balances prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful. For example, the president can veto laws passed by Congress, but Congress can override a veto with a two-thirds vote.
The Bill of Rights and Individual Liberties
The Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments to the Constitution, protects individual liberties such as:
- Freedom of speech, religion, and the press
- The right to bear arms
- Protection against unreasonable searches and seizures
- The right to a fair trial
The Bill of Rights has been used to protect individual freedoms in numerous cases, including:
- Tinker v. Des Moines Independent Community School District(1969): Students’ right to wear armbands in protest of the Vietnam War
- Miranda v. Arizona(1966): Suspects’ right to be informed of their rights before being questioned
The Impact of the Constitution on American Society and History
The Constitution has had a profound impact on American society and history:
- It has shaped the development of American institutions, laws, and culture.
- It has been interpreted and adapted to meet changing circumstances, such as the Civil War and the New Deal.
- It has served as a model for other constitutions around the world.
Quick FAQs
What were the key weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation?
The Articles of Confederation established a weak central government with limited powers, leading to issues with taxation, commerce, and foreign policy.
How did the Constitution address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation?
The Constitution created a stronger central government with expanded powers, including the ability to tax, regulate commerce, and conduct foreign policy.
What is the significance of the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights protects individual liberties by limiting the powers of the government and guaranteeing fundamental freedoms.
